Injection molding offers high precision, fast production, and cost-efficiency for creating complex plastic parts in large quantities.
Overview of Injection Molding Process
Basic Principles of Injection Molding
Injection molding is a method for producing parts by injecting material into a mold. This process suits mass production of plastic parts with high precision. It involves these key steps:
Melting: Heat plastic pellets to a molten state.
Injecting: Force the molten plastic into a mold cavity.
Cooling: Let the plastic cool and solidify.
Ejecting: Remove the solid part from the mold.
Important aspects include:
Cycle Time: Ranges from 15 seconds to a few minutes.
Efficiency: Produces thousands of parts per hour.
Precision: Achieves tolerances up to ±0.005 inches.
Key Components of an Injection Molding Machine

An injection molding machine consists of several crucial components:
Hopper: Where plastic pellets enter the machine.
Heater: Melts the pellets.
Injection Unit: Pushes molten plastic into the mold.
Clamping Unit: Holds the mold tightly during injection.
Mold: Custom-made to shape the final product.
Each component’s role is significant:
Power Consumption: Depends on machine size, typically high.
Maintenance: Regular checks are vital for performance.
Advantages of Injection Molding Machines:
Versatile: Processes various plastic materials.
Fast: Offers high-speed production.
Quality: Yields parts with excellent finish.
For more, visit Injection Molding on Wikipedia.
Advantages of Injection Molding in Manufacturing
High Efficiency and Productivity
Injection molding is renowned for its exceptional efficiency and productivity. Key factors contributing to this include:
Cycle Time: Typically between 15 seconds to a few minutes, enabling the production of large quantities in a short time.
Automation: High level of automation reduces labor costs and increases consistency.
Energy Consumption: While variable, modern energy-efficient machines significantly reduce power usage.
Precision and Consistency in Mass Production
The precision and consistency achievable with injection molding are unmatched, especially in mass production. Essential aspects include:
Tolerances: Capable of achieving tight tolerances, often within ±0.005 inches.
Repeatability: High consistency in producing identical parts, crucial for large-scale production.
Material Usage: Efficient use of materials with minimal wastage.
Comparison Table:
| Feature | Details | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Cycle Time | 15 seconds to a few minutes | Enables rapid mass production |
| Automation | High level | Reduces labor costs, increases consistency |
| Tolerances | As tight as ±0.005 inches | Ensures precision in product dimensions |
| Repeatability | High | Crucial for consistent quality in large batches |
| Energy Consumption | Varies, modern machines are more efficient | Reduces operational costs |
For a deeper understanding, check out the Injection Molding Wikipedia page.
Material and Design Versatility
Range of Materials Suitable for Injection Molding
Injection molding is compatible with a wide variety of materials, broadening its application across industries. These materials include:
Thermoplastics: Such as ABS, Polyethylene (PE), and Polycarbonate (PC).
Thermosetting Plastics: Like Epoxy and Phenolic.
Elastomers: Including Silicone and Rubber.
Each material has unique properties:
ABS: Offers good toughness and impact resistance.
Polyethylene: Known for its flexibility and chemical resistance.
Polycarbonate: Provides high strength and temperature resistance.
Design Flexibility and Complexity in Injection Molded Parts
Injection molding supports complex designs and intricate details. This versatility allows for:
Complex Geometries: Can create detailed and intricate shapes.
Surface Finish: Achieves high-quality finishes, including glossy, textured, or matte.
Insert Molding: Incorporates different materials or components into a single part.
Design Considerations:
Mold Design: Critical for achieving desired part characteristics.
Tolerance Levels: Tight tolerances up to ±0.005 inches are achievable.
Part Size: Capable of producing both small and large parts.
For more insights, check Injection Molding on Wikipedia.
Quality and Strength of Injection Molded Products
Durability and Reliability of Products
Injection molding produces parts known for their durability and reliability. Key aspects contributing to this include:
Material Strength: Uses robust materials like ABS and Polycarbonate, ensuring long-term durability.
Design Integrity: Maintains consistency in design, crucial for functional and mechanical parts.
Lifespan: Products typically have an extended lifespan, withstanding wear and tear.
Factors Impacting Durability:
Resin Selection: Choosing the right material affects the product’s lifespan.
Molding Parameters: Optimal temperature and pressure settings ensure strong bonds in the material.
Surface Finish and Aesthetic Appeal
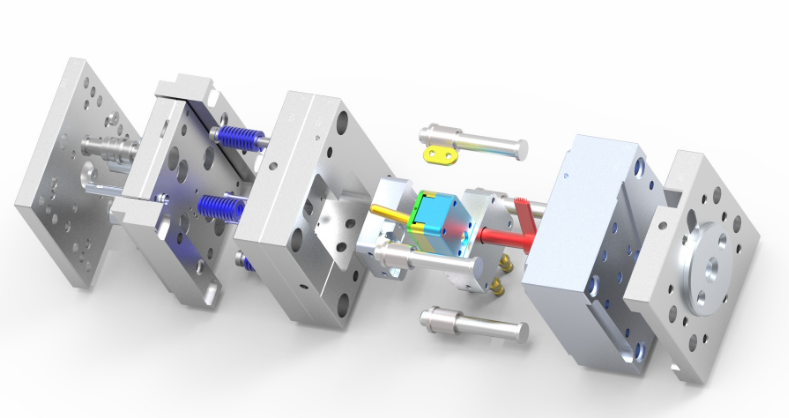
Injection molding also excels in providing excellent surface finishes, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of products. This involves:
High-Quality Finish: Capable of producing smooth, textured, or glossy finishes.
Color Integration: Allows for color integration directly into the mold, ensuring uniform color distribution.
Detail Reproduction: Accurately replicates fine details and textures.
Aspects Affecting Aesthetics:
Mold Design: A well-designed mold is crucial for achieving desired finishes.
Processing Techniques: Techniques like overmolding can enhance aesthetic properties.
Advantages in Aesthetics:
Customization: Offers extensive customization options in terms of color and finish.
Brand Representation: Ideal for creating visually appealing products that represent brand identity.
For further details, explore Injection Molding on Wikipedia.




