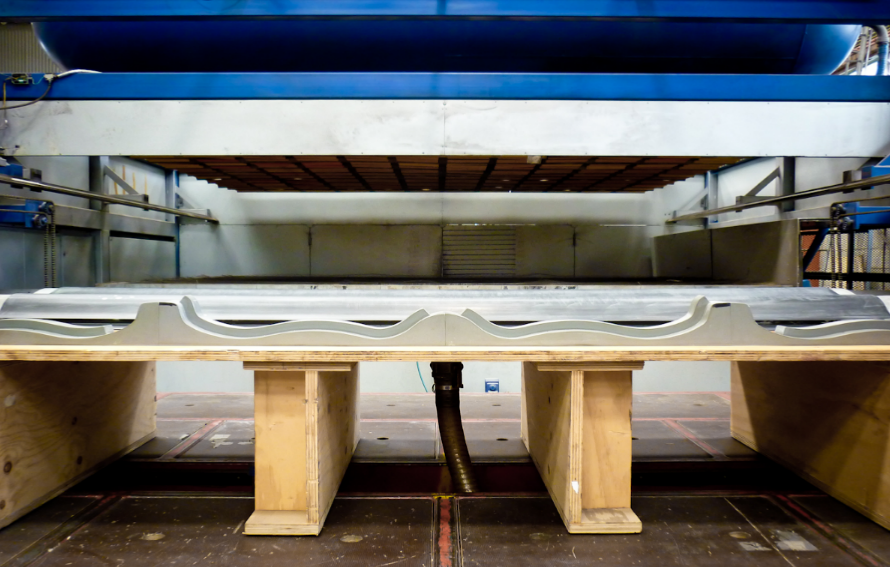
Vacuum forming costs vary based on material, design, and quantity. It’s cost-effective for small batches with tooling costs from $1,000 to $5,000, cheaper than injection molding.
Factors Influencing the Cost of Vacuum Forming
Vacuum forming is a popular plastic molding technique that offers versatility and cost-effectiveness. However, the overall price of a vacuum forming project can vary significantly based on multiple factors. Let’s dive deeper into these variables.
Materials Used
The type and quality of materials play a pivotal role in the overall cost. Common materials like PETG, ABS, and polystyrene come at different price points. For instance:
- PETG: Often preferred for its clarity and deep draw capabilities. As of 2021, its average price ranged between $1.50 to $3 per pound. PETG on Wikipedia
- ABS: Known for its rigidity and toughness. Its average price in 2021 was around $1.20 to $2.50 per pound. ABS on Wikipedia
- Polystyrene: Widely used for its ease of forming and low cost, priced between $1 to $2 per pound.
Size and Complexity of the Project
Larger projects that require intricate details will naturally be more expensive. For example, producing a large vehicle dashboard will be costlier than a simple tray. Complex shapes and features, such as deep undercuts or precise details, might also increase production time, contributing to higher costs.
Labor Costs
Wages vary based on the region and expertise of the workforce. In countries or areas with higher living standards, labor costs might be a significant portion of the project expense. For instance, as of 2021, the hourly wage for a skilled worker in the U.S. might range from $15 to $30, while in other regions, it could be much lower.
Equipment and Machinery Costs
The type and efficiency of the machine can influence costs. High-end machinery with faster cycle times and energy-saving features might have higher upfront costs but can result in savings in the long run. It’s essential to strike a balance between machinery costs and expected output.
Tooling and Molds
The complexity of the mold and the material from which it’s made can significantly affect costs. Aluminum molds, for instance, are more expensive than composite ones but offer better heat transfer and longer life. For a medium complexity mold, you might expect costs anywhere from $1,000 to $5,000. Tooling on Wikipedia
Quantity of Production
Producing parts in bulk generally reduces the cost per unit. For instance, producing 10,000 pieces might have a per-piece cost of $0.50, while producing only 100 pieces could have a cost of $5 per piece. It’s the economy of scale at work, with fixed costs like mold production being spread out over a larger number of units.
Comparing Vacuum Forming with Other Manufacturing Processes
Understanding the nuances of vacuum forming in comparison with other manufacturing techniques can give stakeholders a better grasp on which method might be more suitable for a particular project. Let’s explore these comparisons in depth.
Advantages of Vacuum Forming in Cost Savings
- Low Tooling Costs: Unlike some other methods, vacuum forming doesn’t require high-priced metals for molds, allowing for cost savings especially for shorter production runs.
- Speed: Vacuum forming can be quicker for producing large quantities of simpler parts, making it an efficient option for specific manufacturing needs.
- Material Flexibility: With vacuum forming, manufacturers can use a variety of thermoplastics, allowing for cost adjustments based on material pricing. Thermoplastics on Wikipedia
Limitations of Vacuum Forming in Relation to Cost
- Precision: Vacuum forming might not achieve the same level of detail and precision as other methods like injection molding, which can sometimes lead to higher costs in post-production adjustments.
- Material Thickness Variability: In vacuum forming, the material thickness might not always be consistent, leading to potential wastage or need for additional processing.
- Larger Upfront Costs: Despite lower tooling costs, initial setup for vacuum forming, especially for custom jobs, can be expensive.
Cost Analysis: Vacuum Forming vs. Injection Molding
- Tooling: Injection molding typically has much higher tooling costs due to the need for metal molds, especially for high precision parts. An average mold can cost anywhere from $12,000 to $80,000, depending on complexity.
- Per Piece Cost: While vacuum forming might have higher per piece costs for small batches, injection molding becomes cost-effective as production volumes increase due to the speed of the process. Injection Molding on Wikipedia
- Setup Time: Injection molding machines usually require a longer setup time, especially for intricate designs.
- Material Use: Vacuum forming might produce more material wastage as compared to injection molding, where excess material can often be recycled directly.
Cost Analysis: Vacuum Forming vs. Thermoforming
- Process Similarities: Both vacuum forming and thermoforming involve heating a plastic sheet and shaping it, but the methods of achieving the final shape differ.
- Detail and Precision: Thermoforming often offers better detail and precision as compared to vacuum forming, making it a preferred choice for more intricate designs.
- Speed: Vacuum forming generally has faster cycle times for simpler parts, while thermoforming might be quicker for more complex pieces due to its precision.
- Cost Implication: Thermoforming molds might be slightly more expensive than vacuum forming molds due to their ability to handle deeper draws and intricate designs.
Potential Cost-Saving Measures in Vacuum Forming
Identifying areas to cut costs without compromising on quality is crucial for businesses looking to optimize their production processes. In vacuum forming, there are several strategies that can significantly reduce expenses.
Bulk Purchasing of Materials
Ordering materials in large quantities often leads to discounted prices. For instance, purchasing polystyrene in bulk can reduce its cost from $2 per pound to perhaps $1.60 or even less, depending on the supplier and the amount ordered. Securing a steady, bulk supply contract with a trusted vendor ensures both consistency in material quality and cost savings. It’s also worth noting that maintaining a good relationship with suppliers can open doors to additional discounts and deals. Bulk purchasing on Wikipedia
Streamlined Production Process
Optimizing the production line can lead to significant savings. This includes:
- Reducing Waste: By minimizing material waste, companies can save a substantial amount on material costs over time.
- Employee Training: Ensuring that employees are well-trained and aware of best practices can reduce mistakes, thereby minimizing wastage and reworks.
- Continuous Monitoring: Employing real-time monitoring systems can help in early detection of issues, preventing potential costly breakdowns or defective productions.
Efficient Tooling and Mold Design
The design of tools and molds is pivotal for efficient production. Advanced software can assist in creating designs that maximize the use of materials, reduce waste, and speed up the production process. For instance, a well-designed mold that costs $3000 but increases the speed of production by 20% can save more in the long run than a cheaper $2000 mold that is less efficient. Mold design on Wikipedia
Energy-Efficient Equipment
Energy consumption is a significant cost in vacuum forming. Employing energy-efficient machinery can reduce electricity bills. For example, machines with variable speed drives or those that use energy-saving heaters can reduce energy consumption by up to 30%. Additionally, maintaining machines regularly ensures they run at peak efficiency, preventing energy wastage. There’s also an environmental benefit, as efficient machines often have a lower carbon footprint.
Case Studies
Case studies offer an in-depth look into practical applications and outcomes of vacuum forming in various industries. Here are three such cases highlighting the efficiency, scalability, and ingenuity of this manufacturing process.

Cost-Effective Packaging Solutions
A startup food company was looking for an affordable way to package its range of organic products. Traditional packaging methods were proving expensive, with costs averaging around $0.70 per package. After consulting with a vacuum forming manufacturer, they transitioned to a tailor-made vacuum-formed packaging solution.
Results:
- The new packaging cost was around $0.45 per package, leading to a saving of $0.25 per unit.
- Enhanced product visibility increased customer engagement and sales.
- The company experienced a 15% increase in sales within three months of introducing the new packaging.
- Annual savings amounted to roughly $75,000 based on their production volume. Packaging on Wikipedia
Large-Scale Component Production
An automotive manufacturer was seeking a more cost-effective method to produce interior components for a new car model. Traditional methods quoted them an average cost of $30 per component.
They turned to vacuum forming, which allowed for a quicker turnaround and reduced costs. The process also enabled the manufacturer to easily modify the design based on feedback without incurring excessive expenses.
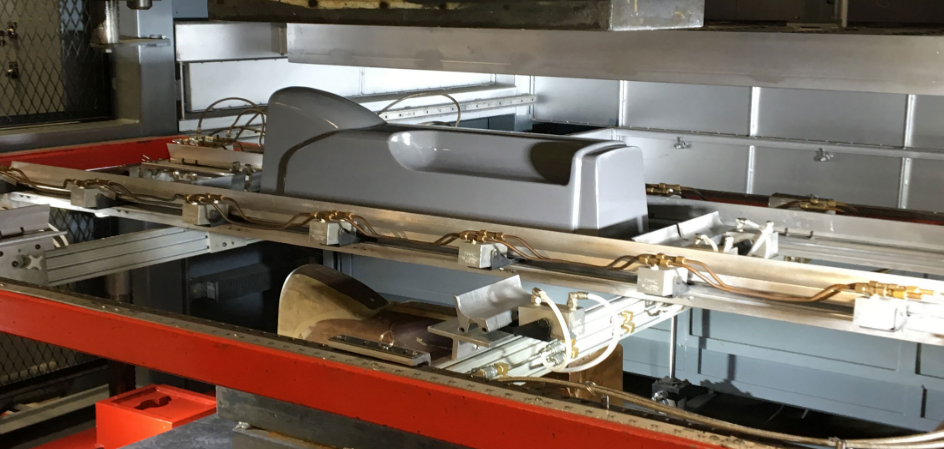

Results:
- The cost was reduced to $22 per component.
- Faster production rates led to meeting tight deadlines.
- The flexibility of the vacuum forming process resulted in a more refined final product. Automotive industry on Wikipedia
Innovative Use of Recycled Materials
A toy manufacturing company was aiming to market an eco-friendly toy line. They decided to explore the possibility of using recycled plastic materials in their production. Vacuum forming presented an opportunity to shape these materials efficiently.
After teaming up with a local recycling facility, they began sourcing post-consumer recycled plastics, leading to both environmental and financial benefits.
Results:
- The cost of raw materials was reduced by 40% as compared to using virgin plastics.
- The toys were marketed as “eco-friendly,” leading to increased brand visibility and customer engagement.
- Sales of the eco-friendly toy line surpassed projections by 20%.





