Injection molds are costly due to intricate design, precision machining, durable materials, and the need for high-quality production.
Cost Factors in Injection Mould Manufacturing
Material Costs for Mould Construction
The choice of materials plays a significant role in the overall cost of injection moulds:

Steel Variants: High-grade metals like stainless steel or hardened steel are common. Their prices can range significantly, from $20 to $200 per square foot, depending on the grade and market conditions.
Aluminum Moulds: Less expensive than steel, aluminum moulds cost about $10 to $100 per square foot. While more cost-effective, they typically have a shorter lifespan.
Specialty Metals: For high-precision or high-volume production, specialty metals like beryllium copper are used in sections of the mould. These materials can significantly increase costs.
Material selection directly impacts the mould’s durability, precision, and cost.
Complexity and Precision Requirements in Mould Design
Mould complexity and precision requirements substantially influence the cost:
Design Complexity: Complex moulds with intricate designs or multiple cavities increase the design and fabrication time, raising costs.
Precision Engineering: High precision requirements for components like gears or threads necessitate advanced machining processes and fine-tuning, which add to the expense.
CAD/CAM Design Costs: Advanced computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software are used for designing these moulds. The sophistication of these tools also adds to the cost.
For more in-depth knowledge, the Wikipedia page on Injection Molding offers valuable insights.
Manufacturing Process of Injection Moulds
The manufacturing process of injection moulds is intricate and labor-intensive. The table below breaks down the key steps, along with associated time and labor considerations:
| Step in Fabrication | Description | Time and Labor Intensity |
|---|---|---|
| Design and Planning | Creating detailed mould designs using CAD software. | High labor intensity for complex designs, taking several days to weeks. |
| Material Selection and Procurement | Choosing appropriate materials based on product requirements. | Time depends on material availability; high precision metals might have longer lead times. |
| Machining and Milling | Cutting and shaping the mould from the raw material. | Highly labor-intensive, can take several weeks depending on mould complexity. |
| Finishing and Polishing | Refining the surface of the mould for quality finishing. | Labor-intensive, can take several days to achieve the desired surface quality. |
| Assembly and Testing | Assembling various mould components and conducting tests. | Time-consuming, especially for complex moulds requiring precise assembly and extensive testing. |
For further details on the injection moulding process, refer to the Wikipedia page on Injection Molding.
Technological Aspects and Equipment in Mould Making
Advanced Machinery and Technology Used in Mould Making
The use of advanced machinery in mould making significantly enhances precision and efficiency:
CNC Machining: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines play a crucial role, capable of precise cutting and shaping with minimal error. The cost of these machines can range from $20,000 to over $100,000.
EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining): Used for detailed and intricate designs, particularly in hard materials. The cost for EDM equipment varies from $30,000 to $150,000.
3D Printing: Increasingly used for prototyping and even producing final moulds, especially for complex geometries. Industrial 3D printers can cost between $10,000 to $500,000.
These technologies contribute to the high cost of mould making but provide unparalleled precision and efficiency.
Maintenance and Upkeep of Mould-Making Equipment
Regular maintenance is vital for the longevity and performance of mould-making equipment:
Routine Servicing: Includes calibration and replacing worn parts. Annual maintenance costs can be about 10-15% of the original equipment cost.
Software Updates: CNC and 3D printing technologies require regular software updates for optimal performance.
Training for Operators: Continuous training is necessary to keep staff updated with the latest technological advancements, adding to the operational costs.
For more detailed insights, explore the Wikipedia page on Moulding.
Economic Considerations of Injection Moulds
Longevity and Durability of Moulds
The lifespan of an injection mould is a critical economic factor:
Steel Moulds: High-grade steel moulds can last for over a million cycles. They are more expensive initially but offer longevity.
Aluminum Moulds: More affordable but typically last for 100,000 to 200,000 cycles. Suitable for shorter runs or prototypes.
Maintenance Impact: Regular maintenance can extend a mould’s life, impacting its overall economic value.
The choice of material and maintenance strategy plays a significant role in the mould’s lifespan, affecting long-term costs.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Mould Investment
A thorough cost-benefit analysis helps justify the high investment in injection moulds:
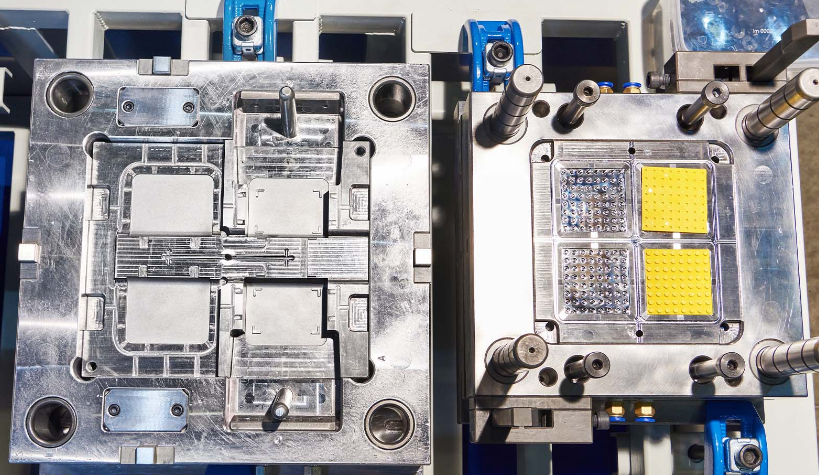
Initial Investment vs. Per-Unit Cost: High upfront cost of moulds can be offset by the low per-unit cost in high-volume production.
Quality vs. Cost: Higher-quality moulds reduce waste and the need for rework, offering better cost efficiency in the long run.
Market Competitiveness: Investing in high-quality moulds can lead to superior products, enhancing market competitiveness.
Investing in quality moulds is often economically justified by lower long-term costs and higher marketability of the final products.
For further insights into the economic aspects of injection moulding, visit the Wikipedia page on Injection Molding.




